What is SIEM? Security Information and Event Management
SIEM stands for security information and event management, and it is a single security management system that provides full visibility into network activities, allowing you to respond to attacks in real-time. It gathers, parses, and categorizes machine data from a variety of sources, then analyzes the information to deliver insights so you may take appropriate action.
How does SIEM work?
SIEM technologies collect event and log data generated by host systems, applications, and security devices such as antivirus filters and firewalls throughout a company's infrastructure and consolidate it on a single platform. Successful and unsuccessful logins, malware activity, and other potentially harmful behavior are all categories that SIEM tools recognize and filter the data into.
When the SIEM software detects possible security concerns, it sends out security alerts. Organizations can assign a low or high priority to these alerts using a set of established guidelines.
A user account that creates 25 unsuccessful login attempts in 25 minutes, for example, may be reported as suspicious but still be assigned a lower priority since the login attempts were most likely conducted by a user who had forgotten his login details.
A user account that generates 130 unsuccessful login attempts in five minutes, on the other hand, would be classified as a high-priority event since it's almost certainly a brute-force assault.
Ready to get started?
Why is SIEM important?
SIEM is significant because it makes it simpler for businesses to manage security by filtering large volumes of data and prioritizing security warnings generated by the program.
Organizations may use SIEM software to detect issues that might otherwise go unnoticed. The program looks at the log entries to see if there are any indications of suspicious activity. Furthermore, because the system collects data from several sources throughout the network, it can reconstruct the timeline of an assault, allowing a corporation to understand the nature of the attack and its financial effect.
A SIEM system may also assist a company in meeting compliance obligations by automatically providing reports that incorporate all of the documented security events from all of these sources, making it a key component of a robust Cyber Assurance Program. The organization would have to manually collect log data and generate reports if it didn't have SIEM software.
A SIEM system also improves incident management by allowing a company's security staff to trace an attack's path throughout the network, identify compromised sources, and give automated capabilities to stop assaults in progress. For more insights and updates on security trends, you can subscribe to our Newsletter
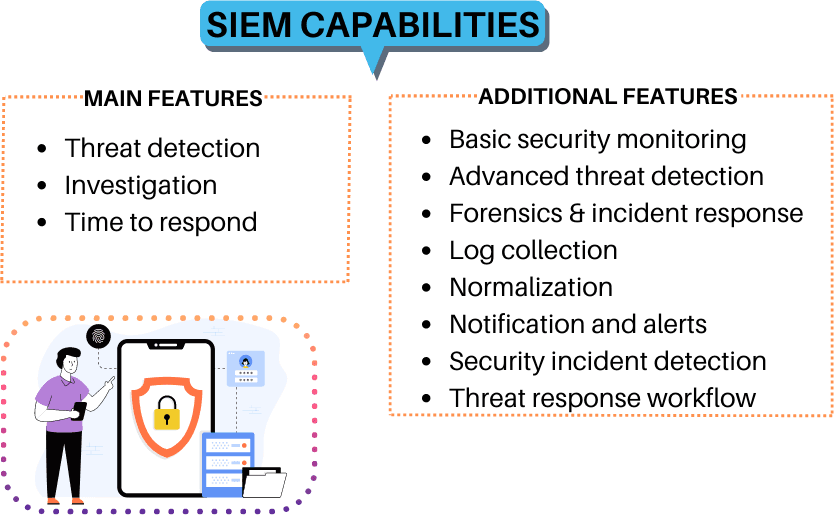
Security Information and Event Management Capabilities
Benefits of SIEM
There are a variety of benefits to running a SIEM solution:
- Advanced Visibility - Aggregating logs from on-premises and cloud-based applications, servers, databases, and more to acquire deeper insights into your users, endpoints, traffic, activity, and more allow you to retain network and perimeter visibility as your organization grows.
- Data Normalization - The various technologies in your environment generate a large amount of data in a variety of formats. While not every SIEM system will automatically gather, parse, and normalize your data, many do provide continual parsing to handle a variety of data formats. This makes data correlation for threat analysis and investigation easier.
- Log Correlation - A SIEM can correlate logs for analysis in addition to collecting them. This makes it possible to create security warnings, trends, and reports. Logs from several hosts provide significantly more context for determining security occurrences. To detect a potential attack, a company can correlate events such as suspicious DNS behavior, unusual port traffic on routers and firewalls, endpoint or antivirus threats, and so on.
- Threat Detection - Threat detection and alerting are achieved through correlation and analysis. You can surface indicators of a compromise or risks that could lead to a breach after a SIEM is correctly set up and tailored to meet your environment. Some SIEMs come with a pre-configured set of alert rules. To limit the noise of alerts that impact your team, discover the correct balance of false positives and false negatives so they know when to take repair action.
- Help Meet Compliance - Many industry-specific compliance laws, such as HIPAA, CMMC, NIST, FFIEC, PCI DSS, and others, require firms to collect and store audit logs for a set amount of time, detect and respond to risks, and provide periodical security reports for auditors.
SIEM Capabilities
Aside from the numerous advantages a SIEM may bring, it's critical to understand what precise features a SIEM possesses that can aid security professionals in their work:
- Data aggregation - Data from multiple systems is consolidated, making searches easier and faster.
- Threat detection - Analyzes data gathered from the environment to uncover unusual trends
- Forensic investigations - Uses modern techniques to conduct in-depth analyses of key security occurrences in order to create unalterable evidence that can be used in court.
- Compliance and auditing - Strong perimeter security, real-time threat detection, visibility into logs, access control, and automated reports and documentation support PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, SOX, and other laws.
SIEM Use Cases
- Monitor, correlate and analyze activity across multiple systems and applications
- Prevent external and internal threats by monitoring the activities of users such as those with privileged access (both internal and third parties), users with access to critical data assets like intellectual property, and executives
- Access to server and database resources is monitored, and data exfiltration is monitored
- Provide compliance reporting
- Protect against IoT threats like denial-of-service attacks by identifying hacked or at-risk devices in the environment
- Improve the orchestration and automation of incident response workflows
Enhance Your SIEM Knowledge with Bootcamps
In addition to implementing a SIEM solution, bootcamps offer practical, hands-on training to help your team gain deeper expertise in cybersecurity, threat detection, and risk management. These programs are designed to equip professionals with the skills needed to leverage SIEM tools effectively and stay ahead of cyber threats.
For advanced protection, consider pairing your SIEM solution with next generation firewalls to strengthen your network perimeter and prevent more sophisticated threats.
Contact
For additional information about anything in this proposal or to purchase Aspire Tech, please contact
Secure your remote workforce
If you're looking to increase protection for your organization.
Investigate Business And Financial Misconduct. Evaluate Opportunities and Analyze Risk. Secure Assets And People. Monitor, Remediate And Recover Assets. Respond To And Investigate Data Breaches.
